A nice overview about the Y2H-system is written by a D. Parchaliuk (Technical Tips Online, 1999):

Information on yeasts as a model for eucaryonts can be found at Rochester University. The Yeast genome database is curated by Stanford University.
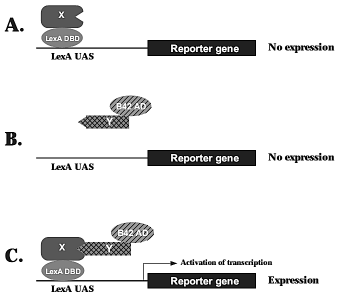
| The objective of the yeast 2-hybrid (Y2H) technique is to screen for or to examine protein-protein interactions. Briefly, a transcription factor (TF) is separated into its DNA binding domain (DBD) and RNA-polymerase activating domain (AD) and separated like this the TF is not active. Now the protein to study is cloned in frame with the DBD (also called "bait") and the second protein (or a cDNA library in the case of a screening) is cloned in frame with the AD (also called "prey"). Each of these chimeric proteins do not act as a functional TF - but when there are protein-protein interactions, then the two parts of the TF are coming closed together and act again as a TF - in this case for reversing auxotrophy, e.g. His, and for a reporter gene, e.g. β-galactosidase. A nice overview about the Y2H-system is written by a D. Parchaliuk (Technical Tips Online, 1999):  Information on yeasts as a model for eucaryonts can be found at Rochester University. The Yeast genome database is curated by Stanford University. |

|
|
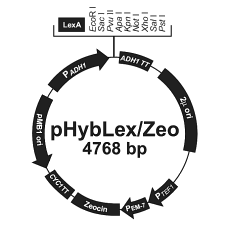
Bait vector: pHybLex/Zeo (pHL) - Promotor: truncated ADH1 (alcohol dehydrogenase) for strong constitutive expression of - LexA ORF: Complete LexA gene (606 bp) - MCS: 9 unique restriction sites: EcoRI, SacI, PvuII, ApaI, Acc65I, NotI, XhoI, SalI, PstI - ADH1 transcription termination: stabilises mRNA - 2µ origin: replication of yeast plasmid (high copy) - Promotor: TEF1 (transcription elongation factor 1) for expresssion of: - Promotor: EM7 (synthetic procariontic promotor) for expression of: - Sh ble gene (Zeocin resistance) - CYC1 transcription termination: stabilises mRNA - ColE1 origin: replication of bacteria plasmid (E. coli) |
 |
|
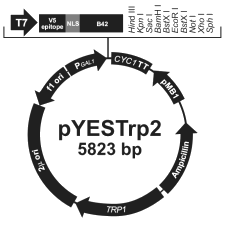
Prey vector I: pYESTrp2 (pYT) - Promotor: GAL1 for strong constitutive expression (within L40) of - V5-epitope: for anti-V5 antibodies - NLS (nuclear localisation sequence): from SV40 large T antigen - B42 ORF - MCS: 8 unique restriction sites: HindIII, Acc65I, SacI, BamHI, EcoRI, NotI, XhoI, SphI - CYC1 transcription termination: stabilises mRNA - ColE1 origin: replication of bacteria plasmid (E. coli) - Ampicillin resistence gene: Selection in E. coli - TRP1 gene: Auxotrophy selection in trp- hosts (like L40) - 2µ origin: replication of yeast plasmid (high copy) - f1 origin: rescue of ssDNA |
 |
|
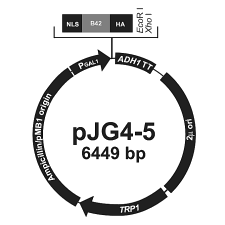
Prey vector II: pJG4-5 (pJG) - Promotor: GAL1 for strong constitutive expression (within L40) of - NLS (nuclear localisation sequence): from SV40 large T antigen - B42 ORF - HA-epitope: for anti-HA (hemagglutinin) antibodies - MCS: 2 unique restriction sites: EcoRI, XhoI - ADH1 transcription termination: stabilises mRNA - 2µ origin: replication of yeast plasmid (high copy) - TRP1 gene: Auxotrophy selection in trp- hosts (like L40) - Ampicillin resistence gene: Selection in E. coli - ColE1 origin: replication of bacteria plasmid (E. coli) |
 |
| YC | Storage at 4 °C |
| 1.2 g | YNB (Yeast Nitrogen Base, w/o ammoniumn sulfate and aminoacids) |
| 20.0 g | glucose |
| 5.0 g | (NH4)2SO4 |
| 10.0 g | succinate |
| 6.0 g | NaOH |
| 1.25 g | specific aminoacid mixture (0.1 g and 0.05 g of each aminoacid, respectively) |
| for agarplates: add ~ 15 g agar | |
| adjust vol. to 1,000 ml and autoclave | |
| pour agar plates after cooling down to ~ 50 ºC to avoid condensed water add antibiotics etc. only after autoclaving when cooled down |
|
| 2 ml Zeocin (100 mg/ml) | for YC Z200 plates (=> 200 µg/ml) |
| 2 ml 3-AT (1 M) | for YC -H 3AT plates (=> 200 µg/ml) |
| Zeo stock | Storage at -20 °C |
| 100.0 mg/ml | zeocin in A. dest. (sold steril) |
| add 25 µl to 100 ml low salt-LB => 25 µg/ml add 200 µl to 100 ml YC => 200 µg/ml |
| 1 M 3-AT stock | Storage at 4 °C |
| 1,68 g | 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole in 20 ml A. dest. |
| sterilise by filtration (0.2 µm PES) | |
| add 0.5 ml to 100 ml YC -H => 5 mM |
| aminoacid mixtures | Storage at RT | |
| YC -WHUK | 1.0 g each: Ade, Arg, Cys, Leu, Thr | 0.5 g each: Asp, Ile, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Val |
| YC -HUK | 1.0 g each: Ade, Arg, Cys, Leu, Thr, Trp | 0.5 g each: Asp, Ile, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Val |
| YC -WU | 1.0 g each: Ade, Arg, Cys, Leu, Thr, Lys | 0.5 g each: Asp, Ile, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Val, His |
| YC -W | 1.0 g each: Ade, Arg, Cys, Leu, Thr, Lys, Ura | 0.5 g each: Asp, Ile, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Val, His |
| YC | 1.0 g each: Ade, Arg, Cys, Leu, Thr, Lys, Trp, Ura | 0.5 g each: Asp, Ile, Met, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr, Val, His |
| Media usage | Saccharomyces cerevisiae growths at 30 °C and needs about 2 days to grow up. |
| YC | Growth of Sc.c. strain L40 (without selection pressure) |
| YC Z200 | Growth of Sc.c. L40 with pHL-vector (selection pressure for pHL) |
| YC -HUK Z200 | Test of Sc.c. L40 with pHL-vector for autoactivation (selection pressure for pHL and LexA activation) |
| YC -W | Growth of Sc.c. L40 with pYT or pJG-vectors (selection pressure for pYT/pJG) |
| YC -WHUK | Test of Sc.c. L40 with pHL-vector for autoactivation (selection pressure for pYT/pJG and LexA activation) |
| YC -W Z200 | Growth of Sc.c. L40 with pYT/pJG- and pHL-vectors (selection pressure for both pYT/pJG and pHL) |
| YC -WHUK Z200 | Test of Sc.c. L40 with pYT/pJG- and pHL-vector for protein-protein interactions (selection pressure for pYT/pJG and pHL and LexA activation) |
| YC -WHUK Z200 3AT | Test of Sc.c. L40 with pYT/pJG- and pHL-vector for strong protein-protein interactions (selection pressure for pYT/pJG and pHL and LexA activation). The LexA-activation results in His-prototrophy and 3-AT is inhibiting this His-synthesis, thus strong protein-protein interactions are needed to overcome this. |
| PBS | Storage at RT |
| 1.78 g | Na2HPO4 * 2 H2O (0.01 M) |
| 14.61 g | NaCl (0.25 M) |
| adjust vol. to 1000 ml with A. dest. and autoclave |
Introducing the hybrid vector(s) into the yeast cells. Vectors bases on the 2-µm DNA are maintained stable and in high copy number (50 - 100) within the cells.
| 10x LiOAc (1 M) | Storage at RT |
| 10.2 g | Li-acetate (=> 1 M) |
| 90 ml | A. dest |
| adjust with HAc to pH 7.5 | |
| adjust vol. to 100 ml with A. dest. and autoclave |
| LiOAc/TE | Storage at RT |
| 10 ml | 10x LiOAc |
| 10 ml | 10x TE-buffer |
| adjust vol. to 100 ml with A. dest. and autoclave |
| LiOAc/PEG/TE | Storage at RT |
| 20 ml | 10x LiOAc |
| 20 ml | 10x TE-buffer |
| 100 g | PEG 3350 |
| adjust vol. to 200 ml with A. dest. and autoclave Keep bottle tightly closed to prevent evaporation |
| salmon DNA (2 µg/µl) | Storage at -20 °C |
| 20 mg | salmon sperm DNA (herring sperm DNA can also be used) |
| 10 ml | TE-buffer |
| dissolve by stirring overnight at 4 °C boil for 5 min and chill on ice afterwards aliquot a 500 µl portions and congelate |
| 1 M Mannitol | Storage at 4 °C |
| 9,1 g | mannitol |
| 50 ml | A. dest. |
| sterilise by autoclaving |
| YC/Mannitol | Storage at 4 °C |
| 9,1 g | mannitol |
| 50 ml | YC-medium |
| sterilise by autoclaving |
Yeast cells are exposed to a thermic shock (42 °C), which allows the entrance of small DNA
Inoculate colonies from selective YC plates in a test tube with 2 ml of the same YC medium. Let the cells grow for 1 day 30 °C.The aim is to quantificate the searched protein-protein interaction: the stronger the interactions, the better they act as the transcription factor for the synthesis of the β-galactosidase, the more coloured product can be formed within a time.
The principle of the test is that the β-galactosidase hydrolysis the colourless ONPG forming galactose and yellow o-nitrophenol, with absorbs light at 420 nm.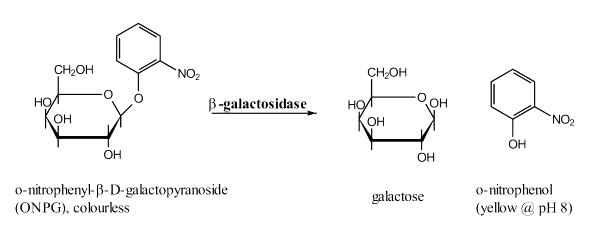
| Z-buffer | Storage at RT |
| 10.68 g | Na2HPO4 * 2 H2O (60 mM) |
| 6.24 g | NaH2PO4 * 2 H2O (40 mM) |
| 0.75 g | KCl (10 mM) |
| 0.246 g | MgSO4 * 7 H2O (1 mM) |
| dissolve in 900 ml A. dest. and adjust pH to 7.0 | |
| adjust vol. to 1000 ml with A. dest. and autoclave |
| Z-buffer/β-ME | prepare daily fresh (50 reactions) |
| 35 ml | Z-buffer |
| 95 µl | β-mercaptoethanol (T) |
| ONPG solution | prepare daily fresh (50 reactions) |
| 32 mg | o-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyranoside |
| 8 ml | Z-buffer (=> 4 mg/ml) |
| 1 M Na2CO3 | prepare daily fresh (50 reactions) |
| 2.12 g | Na2CO3 (Xi) |
| adjust vol. to 20 ml with A. dest. |
| 100 mM PMSF (T, F) | Storage at -20 °C in 100 µl aliquots |
| 17.4 mg | PMSF, Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (T) |
| 1 ml | Isopropanol (F) |
| PMSF, a protease inhibitor, degrades rapidly in water or is inactivated by DTT or β-ME, thus add PMSF right before the cell disruption. A less toxic alternative is AEBSF (4-[2-Aminoethyl]-benzensulfonylfluorid) |
| rel. unit = (A420 * 1000) / (t[min] * 1.5 * OD600) | |